Trophy Hunting








STOP TROPHY HUNTING
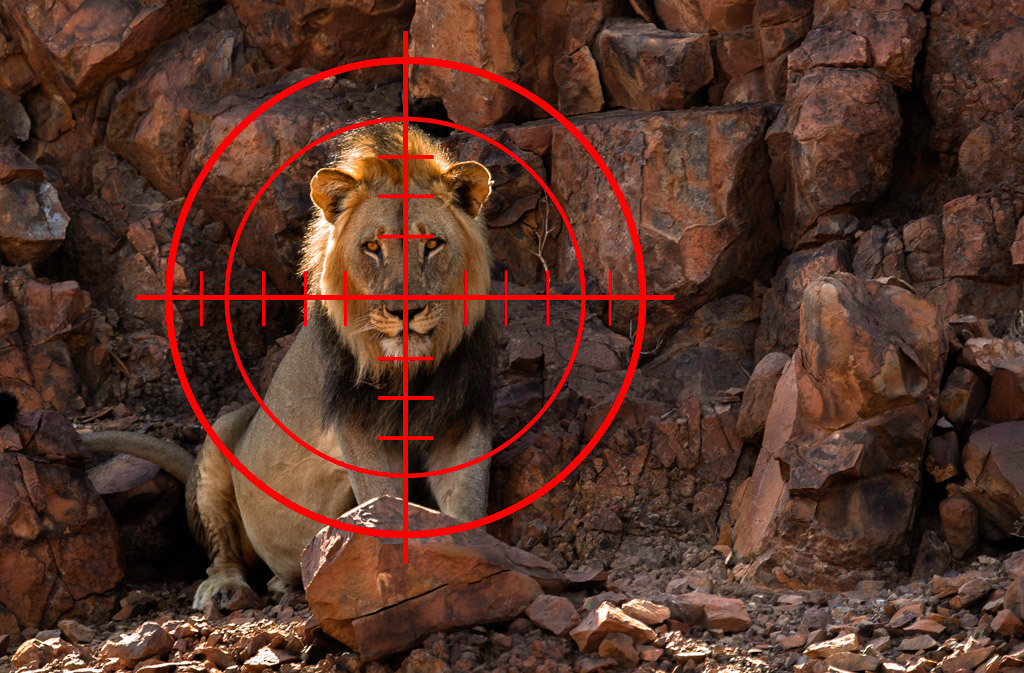
- Threat to Endangered Species: Trophy hunting poses a serious threat to endangered species. Many trophy hunters target rare and threatened species for their exotic appeal or perceived value. Hunting these species can push them further towards extinction, as their populations are often already fragile due to habitat loss, poaching, and other human-induced pressures.
- Disruption of Ecosystems: Predators play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems by controlling prey populations. Trophy hunting disrupts these natural balances by selectively targeting large, dominant animals, often apex predators such as lions, leopards, and bears. The removal of these animals can have cascading effects throughout the ecosystem, leading to population explosions of prey species, loss of biodiversity, and destabilization of food chains.
- Loss of Genetic Diversity: Trophy hunting often targets large, healthy individuals with impressive physical traits, such as tusks, horns, or mane size. These individuals are typically the most genetically fit and play a crucial role in maintaining genetic diversity within their populations. Removing these individuals through hunting can lead to a loss of genetic diversity, making populations more vulnerable to disease, environmental changes, and other threats.
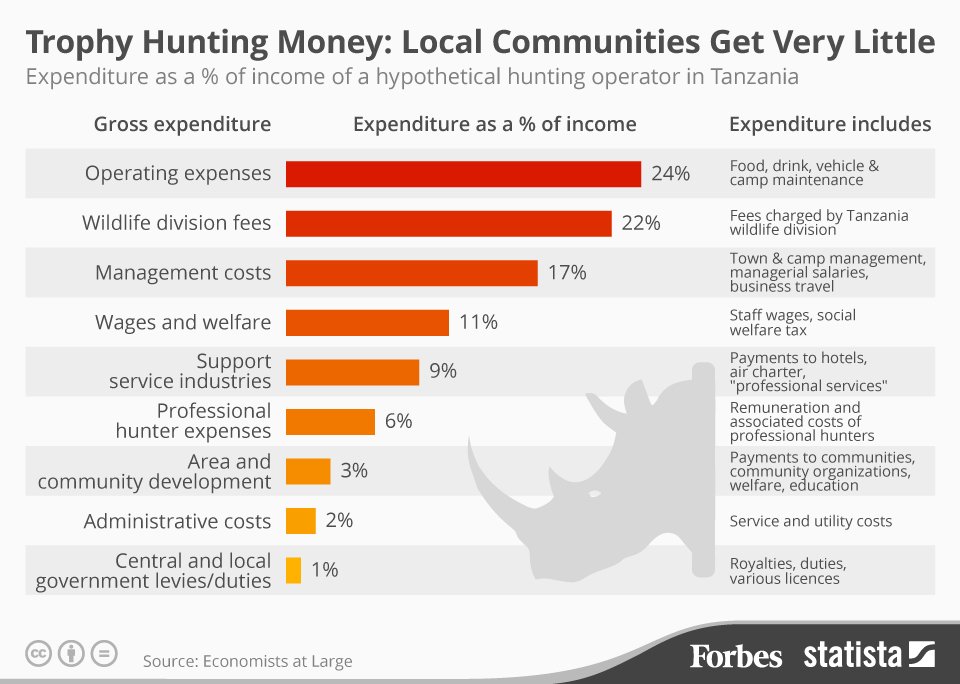
- Economic Myths: Proponents of trophy hunting often argue that it provides economic benefits to local communities and contributes to conservation efforts. However, the economic benefits of trophy hunting are often overstated and fail to outweigh the long-term ecological costs. Additionally, revenue generated from trophy hunting frequently fails to reach local communities or fund conservation initiatives effectively.
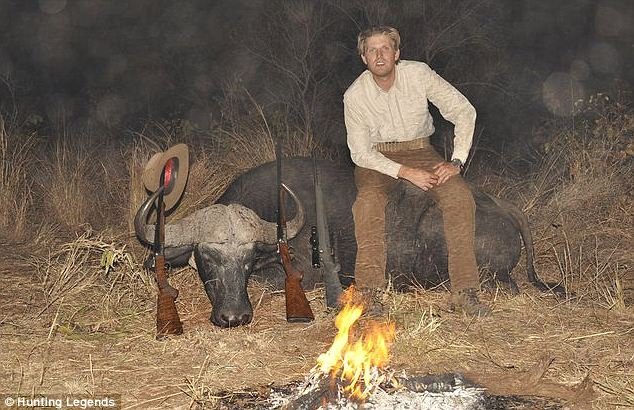
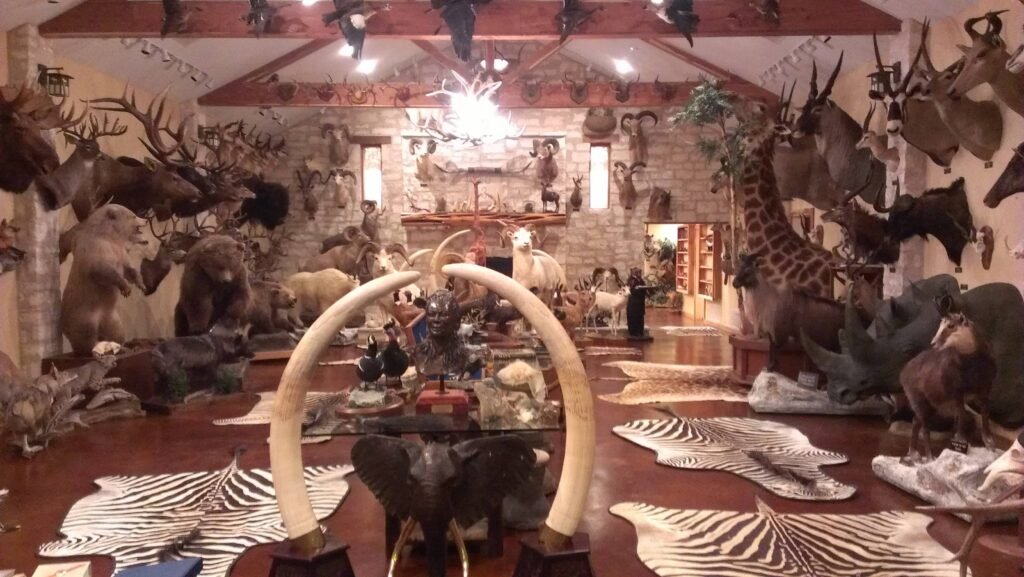
- Ethical Concerns: Beyond its ecological impacts, trophy hunting raises significant ethical concerns. Killing animals for sport and displaying their body parts as trophies is widely regarded as morally unjustifiable, particularly when considering the intelligence, social structures, and capacity for suffering of many targeted species.
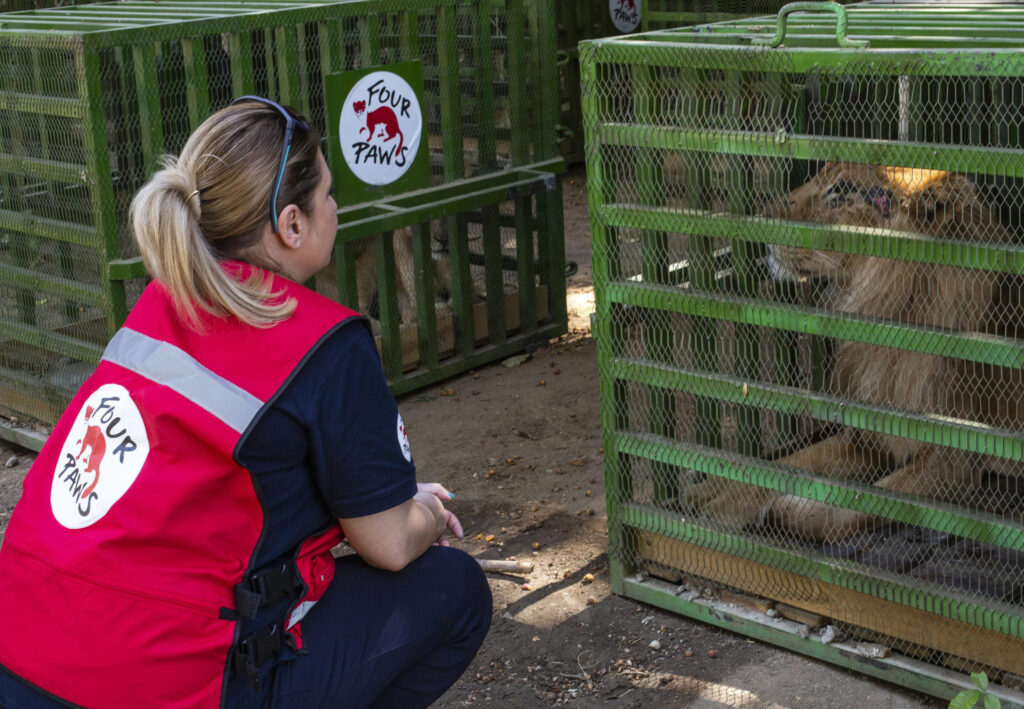
- Alternative Conservation Strategies: There are alternative conservation strategies that have proven to be more effective and sustainable than trophy hunting. These include ecotourism, community-based conservation initiatives, habitat protection, and anti-poaching efforts. These approaches prioritize the preservation of biodiversity and ecosystem health while also supporting local communities and promoting ethical wildlife management practices.
Particularly in the context of trophy hunting and illegal poaching, stems from various ethical, ecological, and conservation concerns. Here are some arguments against lion killing:




-
A Decade On: The Enduring Legacy of Cecil the Lion and the Urgent Call to End Trophy Hunting
Ten years ago, on a quiet evening in the African bush, a single arrow struck Cecil the lion, igniting a […]
-
A Lion’s Intimidating Power Up Close: Meet Guapo of Amakhala
At Sustainable Action Now, while our primary focus often centers on human well-being and environmental justice, we also recognize the […]
-
A Comprehensive Report on Our Urgent Mission for a Thriving Planet Watch SafariLIVE Sunset & Go LIVE at the Waterhole
In an era defined by unprecedented environmental challenges, the call for immediate, decisive action resonates more powerfully than ever. At […]








