In an era defined by rapid global shifts and increasingly visible environmental and social challenges, the clarion call for “Sustainable Action Now” resonates louder than ever. This isn’t merely a slogan; it’s an urgent directive, a foundational principle guiding us towards a future where prosperity, environmental health, and social equity are not just aspirations, but lived realities for all. At its core, Sustainable Action Now embodies the commitment to transform intention into tangible progress, recognizing that the time for debate has passed, and the moment for decisive action is upon us.
Our journey towards true sustainability demands a holistic perspective, one that transcends simplistic notions of “going green.” It encompasses the intricate interplay of environmental stewardship, economic viability, and social justice. Each of these pillars is interdependent, forming the bedrock of resilient communities and a thriving planet. Without environmental health, economic stability is jeopardized; without social equity, the benefits of progress are unevenly distributed, fostering instability. This comprehensive vision is precisely what Sustainable Action Now champions.
The Pillars of Sustainable Action: Beyond Green Initiatives
Environmental Stewardship: Protecting Our Planetary Life Support
At the heart of sustainable action lies a profound responsibility to our planet. This pillar focuses on minimizing our ecological footprint, preserving biodiversity, and ensuring the long-term health of natural ecosystems. Key areas of focus include:
- Decarbonization and Renewable Energy Transition: Accelerating the shift away from fossil fuels towards clean, renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and geothermal power. This involves investing in smart grids, promoting energy efficiency in buildings and transportation, and supporting groundbreaking research into next-generation energy technologies.
- Circular Economy Principles: Moving beyond the traditional “take-make-dispose” model to one that prioritizes reducing waste, reusing materials, and recycling resources. This requires innovative product design, robust recycling infrastructure, and a cultural shift towards valuing longevity and resource efficiency.
- Water Conservation and Management: Safeguarding our most precious resource through efficient irrigation, wastewater treatment, stormwater management, and the protection of freshwater ecosystems. Sustainable water practices are critical for agriculture, industry, and human consumption, especially in the face of changing climate patterns.
- Biodiversity Preservation: Protecting the rich tapestry of life on Earth, from majestic forests to microscopic organisms, which are essential for ecosystem services like pollination, climate regulation, and soil fertility. This involves habitat restoration, combating deforestation, and supporting conservation efforts worldwide.
- Pollution Reduction: Mitigating air, water, and soil pollution through stricter regulations, cleaner industrial processes, and responsible waste disposal. The health of our environment directly impacts human health, making pollution control a vital component of sustainable action.
Economic Viability: Building Resilient and Equitable Economies
Sustainable action also dictates the creation of economies that are not only prosperous but also resilient, inclusive, and equitable. This means rethinking traditional growth models to incorporate social and environmental costs and benefits.
- Green Job Creation: Fostering industries and sectors that directly contribute to environmental protection and restoration. This includes roles in renewable energy installation, sustainable agriculture, ecological engineering, and environmental consulting, providing new pathways to economic opportunity.
- Sustainable Supply Chains: Encouraging businesses to adopt ethical and environmentally responsible practices throughout their entire supply chain, from sourcing raw materials to product delivery and end-of-life management. This enhances transparency, reduces exploitation, and minimizes environmental harm.
- Impact Investing and Sustainable Finance: Directing capital towards businesses and projects that generate positive social and environmental impact alongside financial returns. This shifts investment paradigms from purely profit-driven motives to those that prioritize collective well-being.
- Local Economic Resilience: Supporting local businesses, encouraging community-based enterprises, and building diversified economies that are less susceptible to external shocks. This strengthens local employment, keeps wealth circulating within communities, and reduces reliance on long, carbon-intensive supply chains.
Social Equity and Justice: Ensuring No One Is Left Behind
True sustainability cannot be achieved without addressing systemic inequalities and ensuring that all individuals and communities have the opportunity to thrive. This pillar emphasizes fairness, human rights, and community empowerment.
- Access to Basic Needs: Guaranteeing universal access to clean water, nutritious food, affordable housing, quality education, and healthcare. These are fundamental rights and prerequisites for any community to engage in and benefit from sustainable development.
- Inclusive Governance and Participation: Empowering marginalized communities and ensuring their voices are heard in decision-making processes that affect their lives. This includes fostering democratic participation, supporting indigenous rights, and promoting diversity in leadership.
- Just Transition: Ensuring that the shift to a sustainable economy does not leave behind workers or communities dependent on industries undergoing transformation. This involves retraining programs, economic diversification initiatives, and social safety nets to support equitable transitions.
- Health and Well-being: Creating environments that promote physical and mental health for all, addressing environmental injustices that disproportionately affect vulnerable populations. Access to green spaces, clean air, and safe living conditions are critical components of a sustainable society.
Policy as a Catalyst for Sustainable Action
While individual choices and corporate responsibility are crucial, the scale and urgency of today’s challenges demand robust policy frameworks. Governments play a pivotal role in setting standards, allocating resources, and creating an enabling environment for widespread sustainable action. Policies can incentivize innovation, regulate harmful practices, and guide societal behavior towards more sustainable pathways.
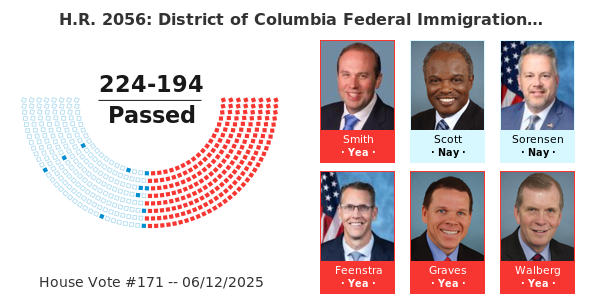
Consider the ongoing legislative efforts that, while seemingly distinct, can have profound implications for community stability and resource management – key elements of social and, by extension, overall sustainability. For example, the District of Columbia Federal Immigration Compliance Act (HR 2056) – Passage Passed – House represents a legislative move with significant social implications. While primarily focused on immigration enforcement, such policies intersect with sustainability by influencing population distribution, resource demand in specific areas, and the social fabric of communities. The stability and well-being of all residents, regardless of immigration status, contribute to a community’s overall resilience and capacity for sustainable development. Policies that foster stable, healthy communities are integral to the broader “Sustainable Action Now” mandate. You can learn more about how policy impacts sustainable development and find resources for engaging with legislative efforts at https://sustainableactionnow.org/.
Effective policy is not just about mandates; it’s about fostering collaboration between government, civil society, and the private sector to build a shared vision for a sustainable future.
The Urgency of “Now”: Seizing the Moment
The “Now” in Sustainable Action Now is not merely a temporal indicator; it’s a call to profound, immediate transformation. We are at a critical juncture where delaying action will lead to irreversible consequences. The scientific consensus on climate change is unequivocal, resource depletion is accelerating, and social disparities are widening.
Every day presents an opportunity to choose a more sustainable path. This means:
- Individual Empowerment: Making conscious consumer choices, reducing personal waste, conserving energy, and advocating for change within our communities.
- Corporate Accountability: Businesses embracing sustainability as a core value, integrating environmental and social considerations into their operations and business models. This includes transparent reporting, ethical sourcing, and investing in sustainable innovation.
- Collective Advocacy: Uniting our voices to demand bolder action from policymakers, holding institutions accountable, and participating in movements that drive systemic change.
Join the Movement: Your Role in Sustainable Action Now
The challenge of achieving true sustainability is immense, but so too is our collective capacity for innovation, collaboration, and change. Sustainable Action Now is more than a concept; it’s a movement built on the belief that a better future is not just possible, but within our grasp, provided we act decisively and together.
We invite you to explore the myriad ways you can contribute to this vital mission. Whether you are a policymaker, a business leader, a student, an activist, or a concerned citizen, your actions, big or small, contribute to the cumulative impact we so desperately need. Discover tools, resources, and inspiration to accelerate sustainable action in your sphere of influence by visiting https://sustainableactionnow.org/. Together, we can build a world that thrives, ensuring a sustainable legacy for generations to come. The time for Sustainable Action is unequivocally Now.